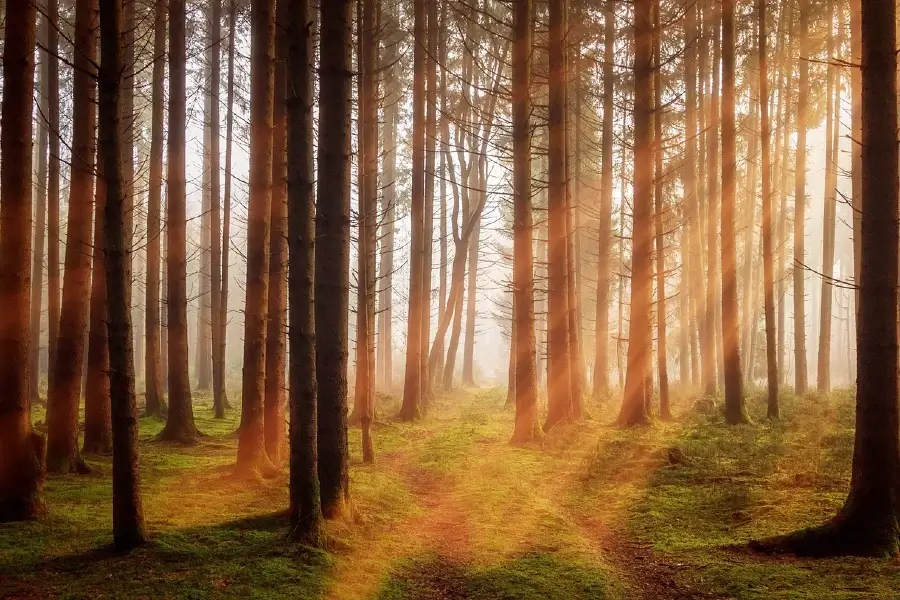
What is Intercanopy Lighting?
Intercanopy lighting is the illumination between the middle layers of a forest canopy, between the uppermost branches (overstory) and the forest floor (understory).
Here’s an overview of the concept:
Forest canopy: The top layer of leaves and branches of a forest that forms a roof-like structure.
Intercanopy: The gap between a tree’s top branches (overstory) and the lower vegetation or forest floor.
Light Penetration:
Sunlight is the primary source of light in a forest. However, the dense vegetation of the overstory prevents a considerable percentage of the light from reaching the forest floor. Intercanopy lighting focuses on the illumination of the intermediate zone.
The importance of inter-canopy lighting:
Plant Growth: In the inner canopy zone, plants rely on filtered sunlight that passes through the overstory. Intercanopy illumination is critical in promoting plant growth.
Forest Ecology: Light conditions in the inner canopy zone affect the distribution and diversity of plant and animal species in the forest ecosystem. Some species thrive in the dappled light of the inner canopy, while others prefer the understory shade or the direct sunlight of forest clearings.
Factors affecting inter-canopy lighting:
Forest Density: The density of overstory foliage considerably impacts how much light reaches the inner canopy zone. Dense forests will receive less inter-canopy light than open woodlands.
Leaf Shape and Size: The shape and size of leaves in the overstory might affect light penetration. Smaller leaves allow more filtered light to flow, while larger leaves may provide more shadow.
Seasonality: Leaf cover changes throughout the year can impact inter-canopy illumination levels. During the winter, as trees shed their leaves, more light enters the forest canopy, increasing inter-canopy lighting.
Studying Intercanopy Lighting:
Scientists employ a variety of approaches to investigate inter-canopy light conditions, including:
Light meters are instruments used to measure light intensity at various places in the forest canopy.
Remote Sensing: Satellite photography and LiDAR (Light Detection and Ranging) technologies can be used to determine forest canopy structure and intercanopy light levels.
Understanding inter-canopy illumination is essential in many domains, including forestry, ecology, and conservation. It contributes to a better understanding of the complex dynamics of forest ecosystems and the development of sustainable forest management techniques.